By Dr. Gabriel Rodriguez
Introduction
Have you ever wondered why mindfulness meditation seems to have such a profound impact on your well-being? Whether you're a seasoned meditator or a curious novice, understanding the neuroscience behind mindfulness can deepen your practice and enrich your life. In this blog post, we'll delve into the science of "Mindfulness and the Brain," focusing on groundbreaking fMRI studies that illuminate how mindfulness meditation affects key brain regions. So sit back, take a deep breath, and get ready to explore your mind from the inside out.
What is fMRI and How Does it Help?
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging, or fMRI, is a non-invasive technique that allows scientists to map and understand brain activity. By tracking changes in blood flow, fMRI produces a dynamic image of the brain in action.
Importance in Neuroscience: fMRI is a powerful tool that has revolutionized our understanding of brain function and its complexity. Here is a brief overview of the importance of fMRI in neuroscience:
- Non-invasive method to study brain function. fMRI allows researchers to observe activity across the whole brain without needing surgery or injections. This has expanded the horizons of human neuroscience.
- High spatial resolution. fMRI can pinpoint activation in small brain structures and regions a few millimeters in size. This enables studying specific neural circuits.
- Maps brain networks. fMRI can identify connected regions active during tasks like emotion, cognition, perception, and show how brain networks communicate. This sheds light on brain organization.
- Links brain to mind and behavior. By correlating fMRI patterns with mental activities or behavioral outputs, researchers can infer the functions of different brain regions and systems. This elucidates mind-brain relationships.
- Clinical applications. fMRI is used pre-surgically to map eloquent areas of the brain. It aids diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of conditions like stroke, tumors, Alzheimer's and psychiatric disorders.
- Safe and reusable. fMRI uses no radiation, allowing repeated scanning. This enables studying developmental changes, learning, aging, and effects of rehabilitation or drugs on the brain.
- Active research field. Advancements in fMRI technology, analysis methods and applications continue expanding the frontiers of cognitive, clinical and social neuroscience.
Understanding fMRI is crucial when diving into the topic of Mindfulness and the Brain, as it gives us a tangible way to measure and analyze the internal changes that mindfulness brings about.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) allows researchers to observe brain activity during mindfulness meditation. fMRI detects changes in blood flow and oxygenation that occur when brain regions are active. As someone meditates inside an fMRI scanner, researchers can pinpoint which parts of their brain “light up” and are recruited during different meditative techniques.
For mindfulness specifically, fMRI shows heightened activity in prefrontal regions like the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and anterior cingulate cortex. These areas govern executive functions like attention control and cognitive flexibility. Increased activation in these regions implies mindfulness strengthens mental focus and clarity. The insula also activates during mindfulness, reflecting enhanced body awareness. Meanwhile, the amygdala, linked to fear and anxiety, is typically deactivated, suggesting mindfulness curbs emotional reactivity.
Researchers can also study connections between brain networks during meditation using resting-state fMRI. Comparisons between novice and expert meditators further elucidate the neuroplastic changes associated with long-term practice. Altogether, fMRI enables researchers to map the brain circuits activated during mindfulness meditation and understand how sustained practice sculpts neural wiring to enhance attention, resilience and well-being.
The Prefrontal Cortex (PFC) and Mindfulness
When it comes to Mindfulness and the Brain, the Prefrontal Cortex (PFC) is one of the stars of the show. Located at the front of your brain, the PFC is the control center for executive functions such as decision-making, problem-solving, and emotional regulation.
Role in Executive Control: The PFC helps you manage complex tasks and make thoughtful decisions.Activation During Mindfulness: fMRI studies have shown that the PFC lights up during mindfulness meditation, indicating heightened activity.
Metacognitive Awareness: With the activation of the PFC, you're not just being mindful; you’re aware that you’re being mindful, which is a metacognitive skill that helps you control your reactions to your thoughts and feelings.
Mindfulness training engages the PFC, enabling you to harness its power for better emotional and cognitive management.
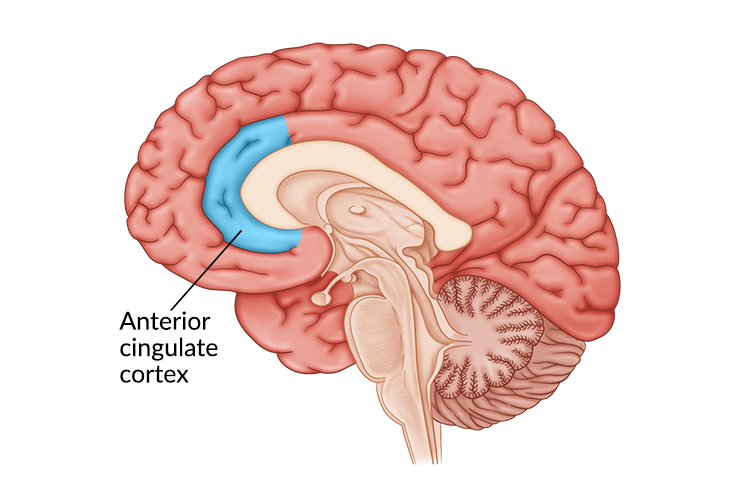
The Anterior Cingulate Cortex (ACC) in Action
Another key player in the world of Mindfulness and the Brain is the Anterior Cingulate Cortex (ACC). Located near the front of the brain, this region is responsible for a wide range of functions, including attention, emotional regulation, and conflict resolution.
Connection with the PFC: The ACC works closely with the PFC to monitor your experiences and adapt behavior accordingly.Activation Patterns: Just like the PFC, the ACC is activated during mindfulness meditation, as evidenced by fMRI scans.
Awareness and Monitoring: The activation of the ACC helps you become more conscious of your thoughts and feelings, providing a heightened state of awareness that’s essential for effective mindfulness practice.
Other Key Regions: Insula and Hippocampus
Mindfulness and the Brain doesn't stop with just the PFC and ACC. Other important regions also come into play.
Insula: Known for its role in emotional awareness and interoception (the sense of the internal state of the body), the insula gets activated during mindfulness practices.Hippocampus: This region is crucial for memory and learning. Mindfulness helps activate the hippocampus, which might explain why regular practice can improve your cognitive abilities.
Both the insula and the hippocampus add to the holistic nature of mindfulness meditation, rounding out its wide range of cognitive and emotional benefits.
Attention, Executive Control, and Emotion Regulation
Let's recap how Mindfulness and the Brain interact in a synergistic dance that boosts various cognitive functions:
Attention: Both the PFC and the ACC contribute to improved focus and attention.
Executive Control: The PFC takes the lead here, making it easier for you to manage complex tasks and make rational decisions.
Emotion Regulation: Activation of these key brain regions during mindfulness helps you gain better control over your emotional reactions.
The interconnected activation of these brain regions produces a tapestry of cognitive and emotional improvements that are too compelling to ignore.
Conclusion
Mindfulness is far more than a buzzword; it’s a practice rooted in neuroscience. From the PFC and ACC to the insula and hippocampus, each activated brain region contributes to the array of benefits that mindfulness meditation offers. The groundbreaking fMRI studies have been invaluable in painting a comprehensive picture of Mindfulness and the Brain. This understanding can help deepen your practice and enhance its effectiveness, offering an array of cognitive and emotional benefits that can transform your life.
What to do next?
Now that you’re equipped with this knowledge, why not take the next step? Consider signing up for a mindfulness meditation course or downloading a guided meditation app to start reaping the cognitive and emotional benefits today. Feel free to share this article with friends or family who might be interested in exploring the fascinating relationship between Mindfulness and the Brain. Remember, mindfulness is a journey, and every step you take is a step towards a better you.
You may also like:
Mind Over Matter: How Mindfulness Meditation May Lead to Structural Brain Changes Over Time: https://newagehealthnwellness.blogspot.com/2023/09/mind-over-matter-how-mindfulness.html






0 comments:
Post a Comment